What Is Temperature Sensor And How Does It Works?
The blog covers what is temperature sensor? And its types.

In this world of internet choosing, a correct informative blog is really very difficult. And once you start reading, they all sound the same. So why not read something interesting.
We have all measured our body temperature at some point; curiosity gets the better of us when we want to know the temperatures of other objects. But our household thermometer is not sufficient. So how could we measure any object's temperature without touching it? Is it possible?
These same questions popped up in my mind until I didn’t encounter a temperature sensor. And today I’m here to let you know what is temperature sensor? How does it work? What are the diverse application areas?
In this guide, we will cover:
- What is the temperature sensor?
- Temperature sensor types.
- Working of the temperature sensor.
1) What Is Temperature Sensor?
Do you know exactly what doe’s sensor do? It converts any physical quantity (like weight, humidity, force, Speed and light intensity) into electrical quantity (like voltage or current).
So as per said what do you think what does temperature sensor do?
You are right, the temperature sensor is an electronic device that converts temperature into an electrical signal.
A temperature sensor is a device which can be a Thermocouple or RTD (Resistive Temperature Detector) that provides temperature measurement in a readable form through an electrical signal.
So this was super easy, that’s not the best part.
The Best part is, what are the different types of temperature sensors?
2) Temperature Sensor Types
Mainly these sensors are categories into two types:
- Contact Temperature sensor.
- Non-contact temperature sensor.
A) Contact Temperature Sensor:
When these sensor comes in contact with an object senses temperature and gives an electrical signal.
E.g. Thermostat, Thermocouple, Thermistors and RTD (Resistive temperature detector).
1) Thermocouple:
The thermocouple is a contact-type temperature sensor, which consists of two different types of metals joined together at one end.
When the junction of the two metals is heated or cooled, a voltage is created that can be correlated back to the temperature.
This happens on account of the phenomena called the thermoelectric effect. Thermocouples are generally inexpensive, as their design and materials are simple.
Just have a look on below image.
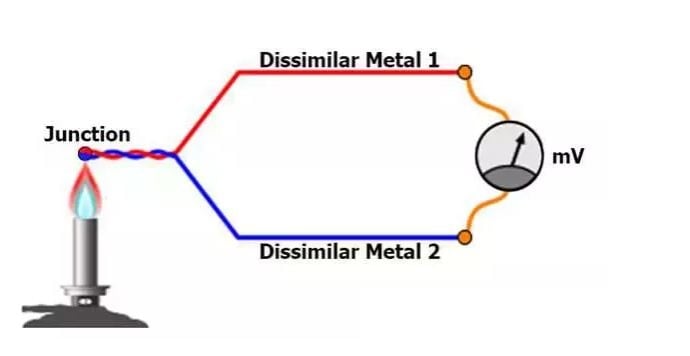
The output of thermocouple depends on the type of thermocouple. The normal thermocouple categories include Types J, K, T, E and N which are known as “Base Metal” thermocouples.
The types R, S and B which are known as “Noble Metal” thermocouples. Also the types C and D which are known as the “Refractory Metal” thermocouples.
The Temperature range of these different sensors is as below:
| Sr. No. | Type | Temperature range |
| 1. | J | 0° to 750°C |
| 2. | K | -200° to 1250°C |
| 3. | E | -200° to 900°C |
| 4. | T | -250° to 350°C |
| 5. | N | 0° to 1250°C |
The Thermocouples that are available in the market,

2) Thermistor:
Another accurate temperature sensor is a thermistor. Thermistors are more precise than thermocouples, and they are made of ceramics or polymers.
The main working principle is, as the temperature changes its resistance also changes.
As per this principle it categories into PTC (Positive Temperature coefficient) and NTC (Negative Temperature coefficient).
In PTC, as temperature increases, the resistance of material also increases.
And same as in NTC, as temperature, decrease the resistance of a material is also decreasing.
Here are some thermistors,
3) RTD (Resistive Temperature Detector):
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD) are essentially the metal counterpart of thermistors, and they are the most precise and expensive type of temperature sensors.
These are made from high purity conducting metal such as platinum, copper or nickel wound into a coil; and whose electrical resistance changes as a function of temperature, similar to that of the thermistor.
Resistive temperature detectors have positive temperature coefficients (PTC) but unlike the thermistor; their output is extremely linear producing very accurate measurements of temperature.
The more common types of RTD’s are made from platinum and are called Platinum Resistance Thermometer or PRT‘s. T
he most commonly available of them all the Pt100 sensor, which has a standard resistance value of 100Ω at 0oC.
The famous RTD’s is here:

4) Thermostat:
The Thermostat is a contact type electro-mechanical temperature sensor or switch; that basically consists of two different metals such as nickel, copper, tungsten or aluminium etc. that are bonded together to form a Bi-metallic strip.
The different linear expansion rates of the two dissimilar metals produce a mechanical bending movement when the strip is subjected to heat.
The thermostat temperature sensor working principle is here,
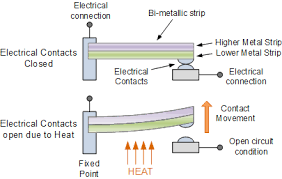
The bimetallic strip can be used itself as an electrical switch or as a mechanical way of operating an electrical switch in thermostatic controls.
The extensive use is to control hot water heating elements in boilers, furnaces; hot water storage tanks as well as in-vehicle radiator cooling systems, In Iron to regulate temperature as per cloths.
B) Non-contact Temperature Sensor
These types of temperature meters are not in direct contact of the object rather, they measure the degree of hotness or coolness through the radiation emitted by the heat source.
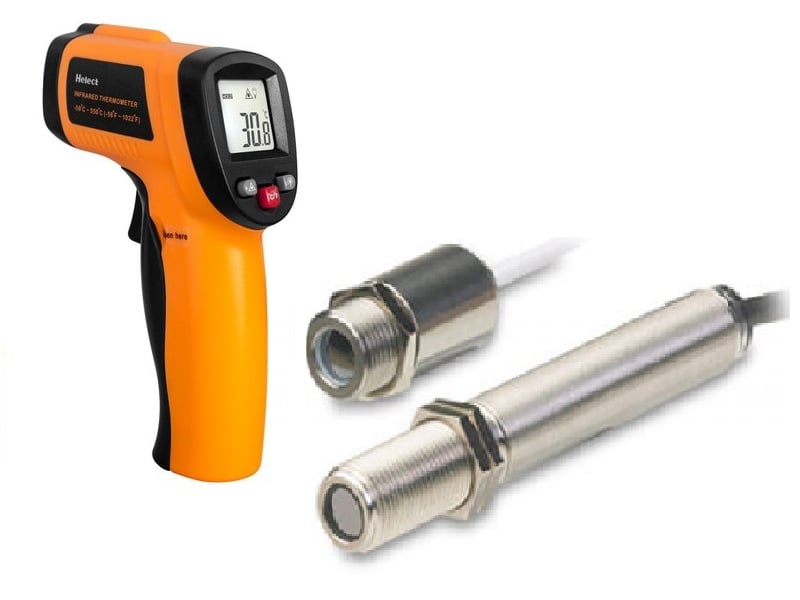

The application area of this non-contact type sensor is wide. During the pandemic Co-vid 19, it helped us so much to test people. There are many more applications just we need to look around.
So now we are well more familiar with the temperature sensor and its various types. We learnt about how do they work also.
If you found that I have missed something here you can write it in the comment below.
To buy such type of temperature sensors click here!








Great post well explained working principle to different types of sensor available and its uses.The best i found in Non contact infrared thermometer.